The cement système de chargement en vrac is a specialized equipment for cement powder. It enables the automatic loading of bulk cement onto vehicles. There are 5 silos in Huaxin (LiJiang)Cement. We carried out corresponding renovations on 5 cement bulk loading systems, which reduced dust emissions, purified the surrounding working environment, and enhanced the market image of the enterprise.
The structural composition of the cement bulk loading machine
The cement bulk loading system is mainly composed of a rotary feeder, a manual spiral gate valve, a pneumatic on-off valve, an air slide chute, a double-layer telescopic chute, a lifting bulk loading head, an automatic material level control switch, dépoussiéreur and an electrical control cabinet, etc.
The rotary feeder can make the cement flow out in a fluid state from silos. It has the functions of stable discharge, mixing and unblocking the hopper.
The manual spiral gate valve can cut off the cement supply when the bulk loading system is under maintenance. But the manual spiral gate valve is usually open during loading.
The valve body of the pneumatic on-off valve is an arc-shaped structure. This allows the cement to flow smoothly and instantly control the start and stop of the filling process.
The loading head is composed of a electric winch and a telescopic chute. The filling is controlled by a material level control switch, and when the filling is complete, a control signal is sent to close the pneumatic on-off valve and stop the loading.
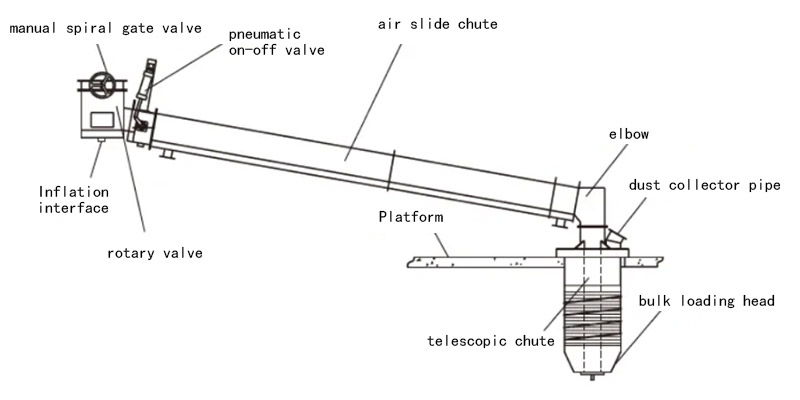
Working Process of the Cement Bulk Loading System
1.Positioning
The driver drives the cement bulk tanker under the fixed bulk loading system. They align the tanker’s feed opening directly beneath the loading head. The operator activates the elevating device. This allows the loading head, connected to the double-layer telescopic chute, to descend into the tanker’s feed opening. After ensuring a tight seal between the loading head and the tanker’s feed opening, the control switch automatically cuts off the power supply. This completes the positioning process.
2.Unloading
Once the loading head is in the designated position, all equipment of the bulk loading machine is sequentially started. The cement is unloaded from the storage in a fluidized state. The fluidized cement passes through the pneumatic on-off valve and the air slide chute into the bulk loader, flowing into the storage tank through the loading head. The dust collector absorbs the gas and dust expelled from the cement transport and the bulk tanker, ensuring a pollution-free work environment. The collected dust is sent to silo for recycle use.
3.Material Level Control
When the cement in the tanker reaches the filling height, the connected air duct installed at the top of the loading head is buried in the cement. The air pressure increases, activating the pressure controller, which sends a signal for a full load control, closing the pneumatic on-off valve to cut off the material source and stopping the loading process. The telescopic chute and loading head are then elevated to complete the loading. Meanwhile, a delay relay is activated to allow the dust collector to continue collecting dust.
4.Departure of the Bulk Truck
After the delay time (generally 4-6 seconds) has elapsed, the dust collector stops. The site bell rings, signaling the end of the bulk loading process. The tanker then drives away.
Perennial Problems
(1) There is “cement clumping” during the loading process. This clumped cement gets loaded into the bulk tanker. It is then transported to the mixing station or construction site for direct use. This affects the quality of the dispatched cement and leads to customer complaints.
(2) During the elevation and descent of the loading head, dust falls from the loading head. This pollution affects the surrounding environment.
(3) During loading, the cement bulk loading system often causes dust emission from the opening of the tanker. This severely impacts the measured values of PM2.5 and PM10 in the surrounding environment.
Analysis of Causes
(1) The cement in the silo often clumps. This is due to factors like rain leakage from the roof, condensation from temperature differences in the walls, high storage temperatures, and crystalline water from gypsum and mixed materials. The clumped cement is usually loosely structured and breaks easily. However, some clumps are more tightly bonded. Using these directly can affect the cement’s quality.
(2) After the pneumatic unloading valve closes, some cement remains in the air slide chute between the valve and the elbow unloading device. During the elevation and descent of the loading head, vibrations or residual air pressure cause the cement in the air slide to flow down and fall to the ground, leading to pollution.
(3) During the bulk loading process, we measured a high negative pressure in the dust collection pipe of the loading head. This indicates that dust escapes from the feed opening of the bulk truck because the spacing between the inner and outer tubes of the loading head is too small. The spacing at the lower end of the loading head is even smaller. This decreases the airflow cross-section of the dust collector’s inlet pipe. As a result, negative pressure in the double-layer telescopic chute increases, reducing airflow into the dust collector. This creates a positive pressure “dust escape” phenomenon in the storage tank of the bulk tanker.
Technical renovation measures
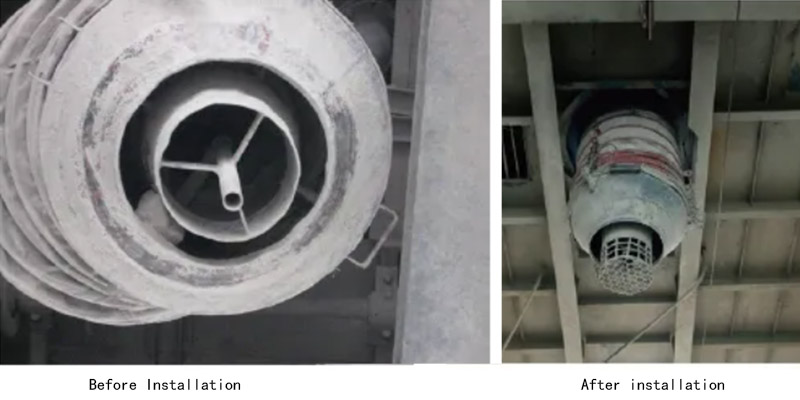
1.Install a screen mesh on the bulk loading head
We design a screen mesh to be installed at the discharge port of the bulk head. The screen mesh has a height of 200 mm. It features a square hole on the side, measuring 30 mm in width and 20 mm in height. Additionally, there is a circular hole on the bottom with a diameter of 25 mm. When cement lumps fall onto the screen mesh inside the tanker, most of the loose lumps are crushed. Only a few stubbornly bonded large pieces remain on the mesh.
After the bulk loading process is completed and the bulk head is lifted, it is easy to notice the residue. This residue can be cleaned promptly before the next loading process.

2.Add another pneumatic on-off valve
We installed a pneumatic on-off valve at the discharge end of the air slide chute. There are two pneumatic on-off valves distributed at both ends of the air slide chute. These two valves will open and close simultaneously to prevent material from spilling out during the lifting process of the bulk head.
We installed a pneumatic on-off valve at the discharge end of the air slide chute. There are two pneumatic on-off valves distributed at both ends of the air slide chute. These two valves will open and close simultaneously to prevent material from spilling out during the lifting process of the bulk head.
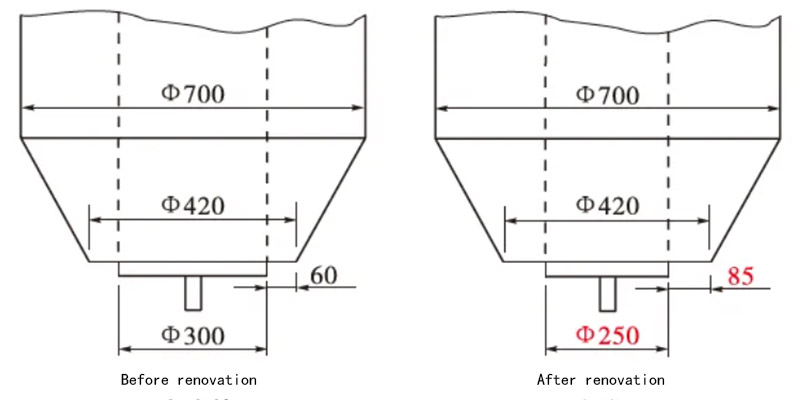
3.Adjust the inner tank of the bulk loading system
We changed the inner tank’s diameter from Φ300 mm to Φ250 mm. This change increases the cross-sectional area of the dust collection duct in the bulk loading system. It also reduces the internal resistance of the dust collection pipe. Additionally, it prevents the occurrence of positive pressure in the storage tank. Practical experience has shown that reducing the diameter has little impact on the cement unloading and loading time.
Result and Evaluation
After the modification was completed, there have been no occurrences of the dust release phenomenon at the bulk truck’s feed inlet during more than a year of bulk operations. We also did not receive any complaint calls from customers regarding cement clumps in the bulk truck. This has improved the work environment, reduced the PM levels in the surrounding area, and enhanced the company’s market image. The technical modification process has yielded satisfactory results.
FAQs
1.How to Ensure bulk loading system’s Long-Term Reliability After the Technical Upgrade?
Long-term stability is key to the success of the upgrade. Our measures include:
Durable Design: We use high-strength steel and quality components, with key drive parts designed to accommodate workload margins, suitable for high-intensity operations.
Intelligent Monitoring: Integration of a fault warning system allows for real-time monitoring of equipment status, enabling early detection of potential issues and reducing unexpected downtime.
Maintenance Optimization: The structural design has been simplified for quick repairs; we also offer remote diagnostics and regular inspection services to lower maintenance costs.
2.Will the Bulk loading system Technical Upgrade Affect the Existing Production Line? How to Evaluate Risks and Costs?
Technical upgrades must balance efficiency improvements with continuity of production. Our assessment process includes:
Demand Analysis: Conduct a thorough investigation of your production process to identify bottlenecks (such as aging equipment or control delays) to ensure the solution is accurately tailored.
Risk Control: Utilize modular design to minimize downtime; provide a detailed implementation plan that includes backup equipment support to prevent production interruptions.
Cost Effectiveness: The solution is cost-efficient, with initial investments quickly recouped through improved efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
3.Our bulk loading system has a slow loading speed, causing vehicles to queue up. How can we improve efficiency through technological upgrades?
The low loading efficiency is usually caused by the limitations of equipment design or control systems. Our technical improvement plan focuses on optimizing the structure of the discharge chute and upgrading the automatic control system. For instance, a multi-section sleeve-type telescopic discharge head is adopted, which can automatically adjust according to the vehicle height, enabling rapid and secure connection and reducing preparation time. At the same time, an integrated intelligent level detection and weight sensing system is integrated, which can automatically adjust the material flow rate, avoiding overloading or underloading, and significantly shortening the single loading cycle.

